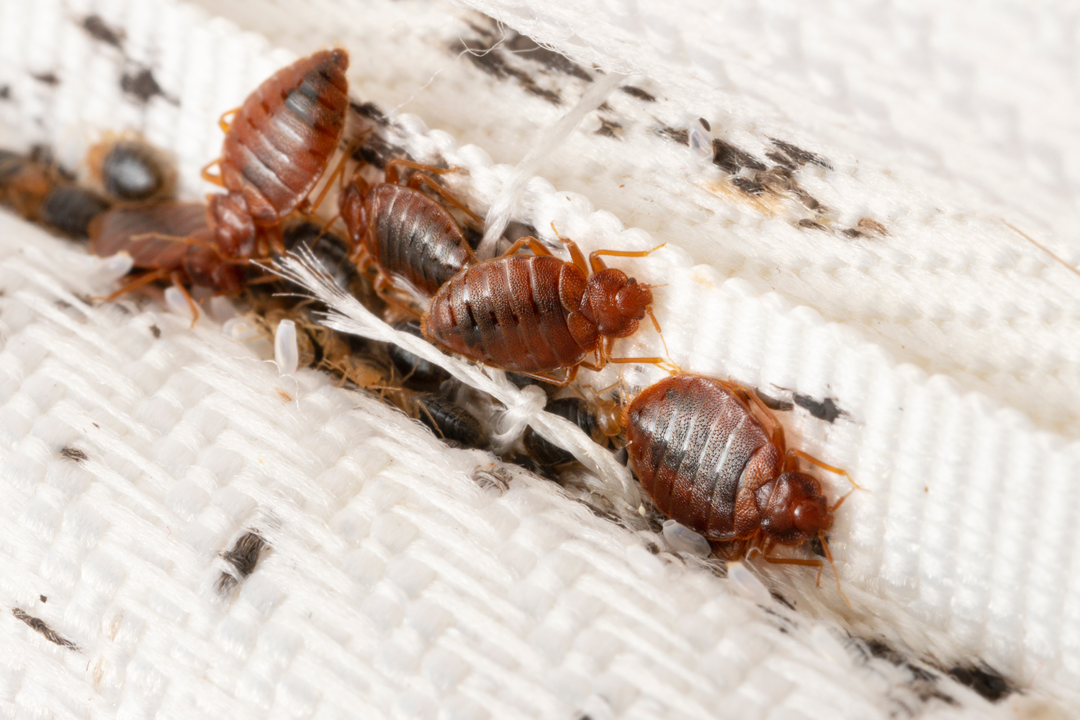
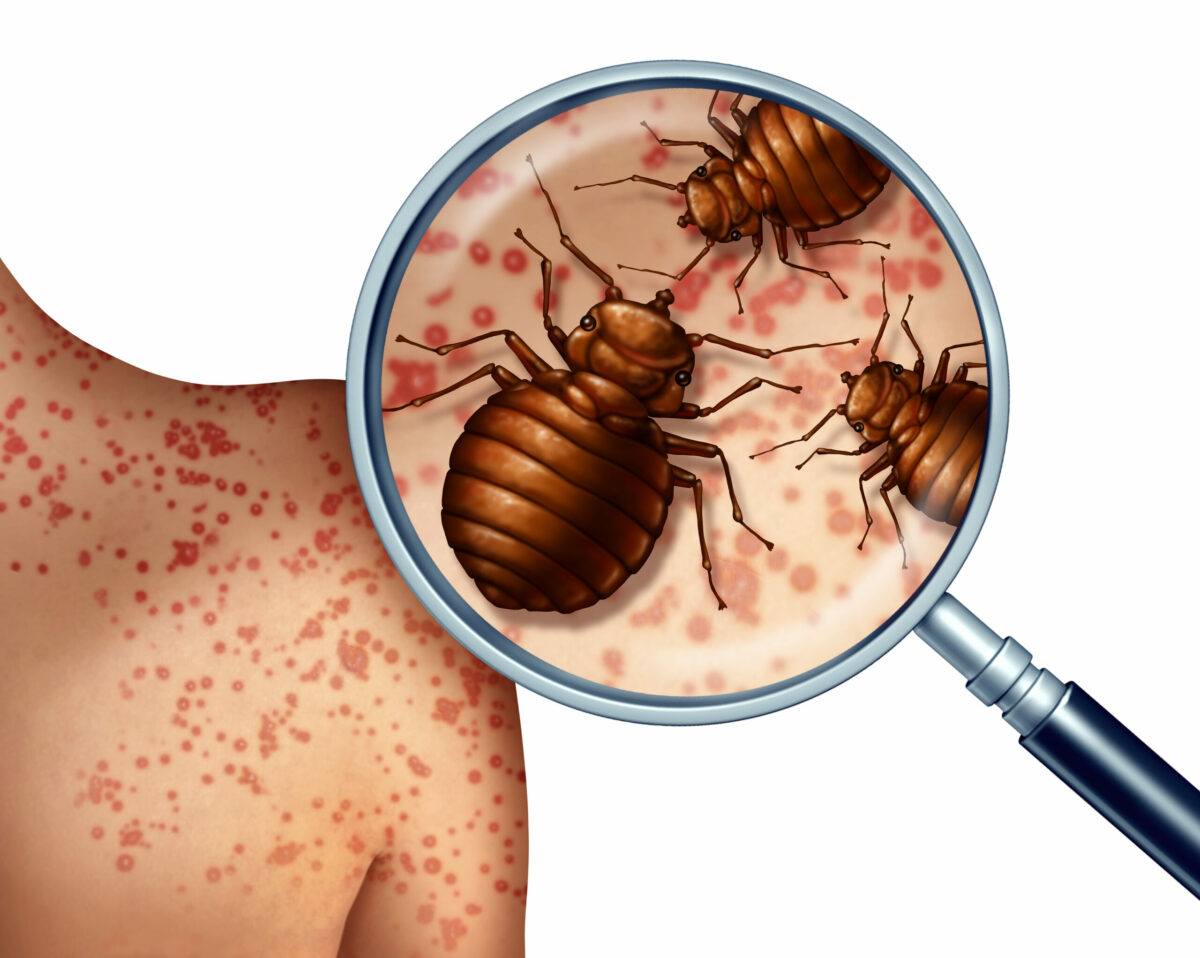
Bed bugs are indeed insects, sharing characteristics typical of the insect class such as having six legs, a three-part body comprising head, thorax, and abdomen, and are wingless in their mature form. These small, nocturnal pests are known for their parasitic habits, particularly their preference for human blood. They have become notorious for their ability to cause infestations in residential spaces as well as commercial lodgings, making them a widespread concern for many.

Understanding the nature of bed bugs is essential in recognizing and controlling infestations. These reddish-brown insects are adept at hiding in cracks, crevices, and anywhere close to where people sleep. Bed bug bites can lead to a range of health implications, including skin rashes and allergic symptoms, which underline the importance of early detection and efficient pest control strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Bed bugs are wingless insects that feed on human blood.
- Their presence can be confirmed through bite symptoms and visual detection in hiding spots.
- Prompt action and effective strategies are crucial for managing bed bug infestations.
Understanding Bed Bugs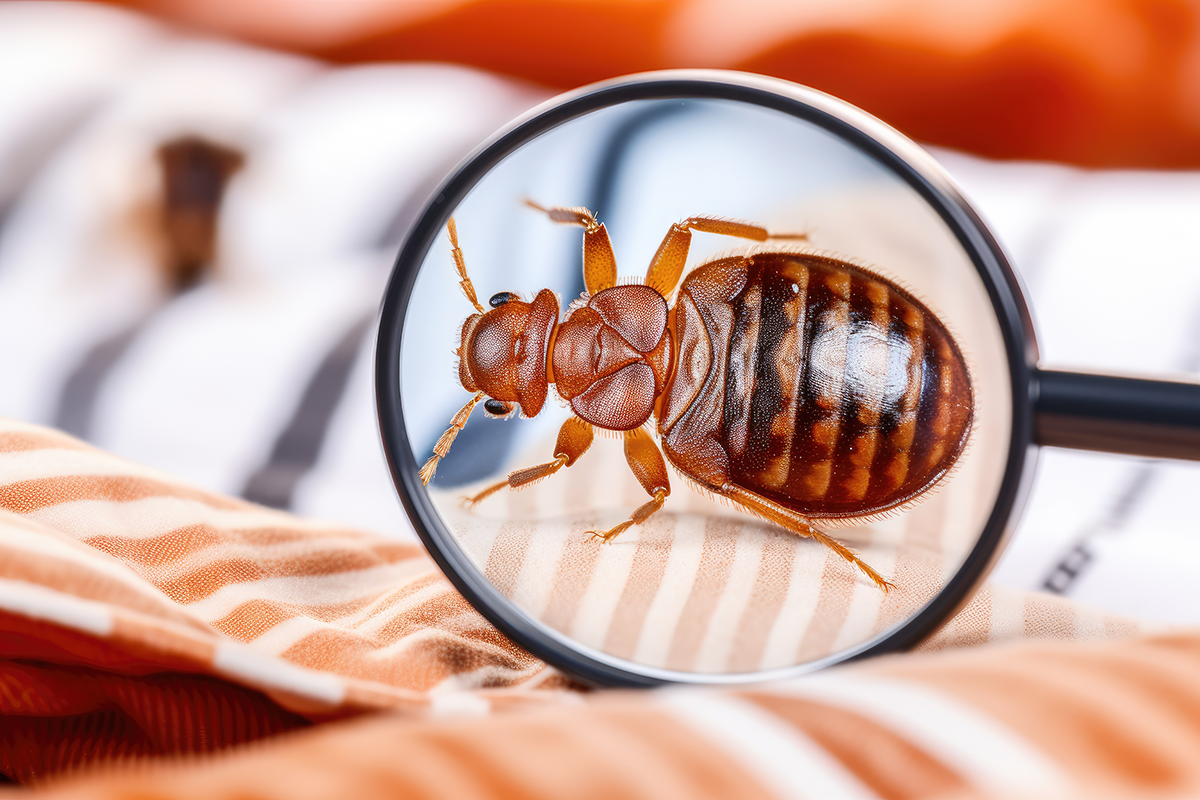
Bed bugs are small, reddish-brown insects known for their dependency on blood meals from humans or other warm-blooded hosts. This section provides detailed insights into their scientific classification, distinct physical characteristics, and their life cycle, which includes development from eggs to reproductive adults.
Scientific Classification
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Insecta
Order: Hemiptera
Family: Cimicidae
Genus: Cimex
Species: Cimex lectularius
The bed bug, primarily the species Cimex lectularius, belongs to the family of insects known as Cimicidae, which are part of the order Hemiptera, commonly referred to as the true bugs.
Physical Characteristics
Bed bugs possess an oval-shaped body with a flattened appearance, allowing them to hide in narrow crevices. An adult bed bug is typically 4-5 millimeters in size, and their color can range from a lighter brown in nymphs to a more reddish-brown hue after feeding on blood.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
- Eggs: Pearly white, roughly 1mm in length, and laid in batches of 1-5 per day.
- Nymphs: Hatch from eggs, resembling miniature adults. They undergo five molt stages before becoming adults, requiring a blood meal before each molt.
- Adults: Fully mature bed bugs can lay up to 500 eggs in their lifetime. The lifespan of an adult can vary but generally ranges from several months to about a year, depending on conditions like temperature and availability of food (blood).
Recognizing Signs of Bed Bugs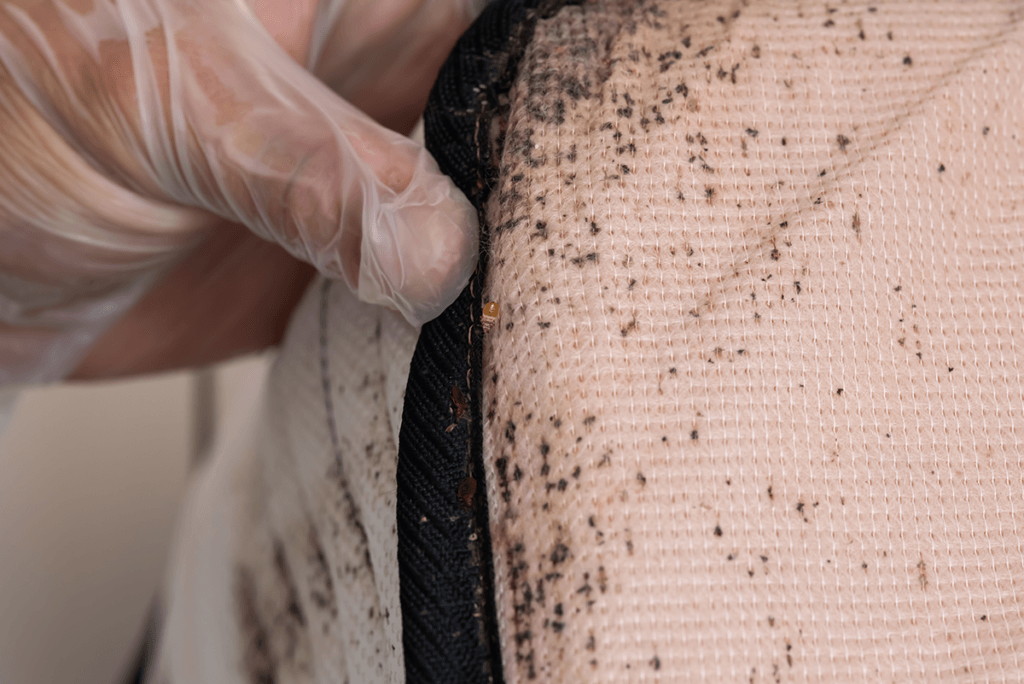
When dealing with bed bug infestations, it’s essential to identify their presence early. One must look for physical signs of bed bugs, which can include bites, marks on bedding, and spotting their typical hiding places. Vigilance in these matters can prevent a more significant problem.
Identifying Bites
Bed bug bites often appear as small, red, and sometimes itchy spots on the skin. They may be found in a line or cluster, usually on areas exposed during sleep. While not everyone reacts to bed bug bites, those who do can experience discomfort, a rash, or in some cases, an allergic reaction.
Common Hiding Places
Bed bugs are adept at concealment, favoring areas like the seams of a mattress, the crevices of a bed frame, and behind the headboard. Inspecting these areas closely, especially within dark and secluded spaces, is key to uncovering an infestation.
Additional Indicators
In addition to bites, other indicators can signal the presence of bed bugs. Small, dark blood stains on bedding from crushed bugs, skin casings shed by nymphs, and a subtle, sweet odor are telltale signs. One may also find tiny black fecal spots in seams or cracks and crevices close to the bed.
Remember, finding signs of bed bugs is the first step in addressing any infestation.
Health Implications of Bed Bug Infestations
While bed bug infestations are often associated with a lack of cleanliness, these determined insects are found in various environments and can lead to a range of health issues, from skin rashes and allergic reactions to psychological distress.
Physical Health Concerns
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are known for their biting habits which typically occur at night. These bites can result in a number of skin-related problems, including red, itchy welts that can cause discomfort. In some cases, individuals may develop an allergic reaction to bites, which can manifest as severe itching, hives, or blisters. While bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases, their bites can lead to secondary skin infections if they are scratched and become open wounds. There have been studies detailing the clinical consequences of bed bug bites which underscore the potential for significant skin irritation and infection.
Psychological Effects
The presence of bed bugs can have substantial psychological effects on individuals, including the development of anxiety and sleep disturbances. The stress of dealing with an infestation and the stigma that might be associated with it can lead to emotional and mental health challenges. Research has delved into the mental health impact of bed bug infestations, outlining various types of distress that affected individuals may experience. Persistent itching and the thought of insects feeding during the night can also contribute to increased levels of stress and anxiety, which can be as debilitating as the physical symptoms.
Prevalence and Spread of Bed Bugs

Bed bugs have become a pervasive issue on a global scale, affecting various types of dwellings and transportation methods. Their ability to hitchhike on personal belongings makes them notorious for spreading easily from place to place.
Global Distribution
Bed bugs are considered cosmopolitan insects, thriving in nearly every region around the world. They are not restricted by geography or climate, which is evident in their widespread presence across continents like North America, Africa, and South America. In the U.S., for instance, there have been significant increases in bed bug infestations in urban environments, particularly in hotels, apartments, and shelters.
Modes of Transportation
These tiny travelers primarily move around through human travel. They can effortlessly latch onto luggage, clothing, and other personal items. This mode of transportation allows them to migrate to new environments, especially those with a high turnover of occupants such as hotels and shelters. Public transportation systems, including buses and trains, are not exempt from these hitchhikers, potentially leading to a wider spread as travelers unknowingly transport them to different locations.
Preventive Measures and Early Detection
Preventive strategies and early detection are crucial in managing bed bug infestations throughout various environments. Acting early can help prevent a larger infestation, which is typically harder and more costly to control.
Protective Actions at Home
Mattresses and Box Springs: Encase mattresses and box springs in bed bug-proof covers. These coverings trap bed bugs inside, making it easier to spot and deal with an infestation early on. Regularly inspect the seams and folds of the coverings for signs of bed bugs.
Furniture and Bedding: Check second-hand furniture thoroughly for bed bugs before bringing it home. Launder bedding at a high temperature frequently to kill any bed bugs that may have made their way to the fabrics.
Declutter: Reduce clutter around the bed to minimize bed bugs’ hiding places. Bed bugs often reside in piles of clothing or other items left near the bed, so maintaining a clean environment constrains their ability to hide and breed.
Inspection Tips for Travelers
Luggage Transport: They should always be cautious when transporting luggage, as bed bugs are notorious for hitching a ride in bags and suitcases. Consider using specialized luggage encasements designed to deter bed bugs.
Hotel Inspection: Upon arrival at a hotel or accommodation, inspect the bed area, including mattress seams, box springs, and headboards, for any signs of bed bugs. Place luggage on a rack away from walls or furniture to avoid easy access for any potential bed bugs.
Professional and DIY Pest Control Strategies
When it comes to managing bed bug infestations, homeowners and pest control professionals have various strategies at their disposal, involving both chemical and non-chemical treatments. These methods aim to effectively target bed bugs in places where they commonly hide, such as mattresses, furniture, and upholstered items.
Chemical Treatments
Professional Chemical Applications: Professionals typically use a combination of insecticides that may include:
- Pyrethroids: Synthetic chemicals that are commonly employed against various types of insects.
- Insect Growth Regulators (IGRs): Which disrupt the growth and reproduction of bed bugs.
Professionals will carefully apply these treatments to infested areas, including seams of mattresses, box springs, bed frames, headboards, and other furniture where bed bugs are found.
DIY Chemical Solutions: Homeowners can opt for over-the-counter insecticide sprays and powders targeting bed bugs. It’s essential they follow the instructions meticulously to avoid misuse and potential harm. Some might try desiccants like diatomaceous earth by sprinkling it around bed frames or upholstered furniture.
Non-Chemical Solutions
Professionals’ Non-Chemical Tactics:
- Heat treatments: Professionals might use specialized equipment to elevate room temperatures to a point where bed bugs cannot survive.
- Vacuuming: This can be effective in physically removing bed bugs from surfaces.
- Encasements: Mattress and box spring encasements are used to trap bed bugs inside and prevent them from escaping.
DIY Approaches:
- Regular Inspection: Checking common hiding spots like bed frames, headboards, and furniture can catch infestations early.
- Washing and Heat-Drying: Bed linens, curtains, and clothes can be laundered in hot water and dried on a high-heat setting to kill bed bugs.
- Freezing: Smaller items might be placed in a freezer at 0°F for at least four days, a method known to kill bed bugs.
Whether choosing a professional service or a DIY route, it’s crucial to combine methods and be diligent in treatment to manage bed bugs effectively.
Understanding Bed Bug Behavior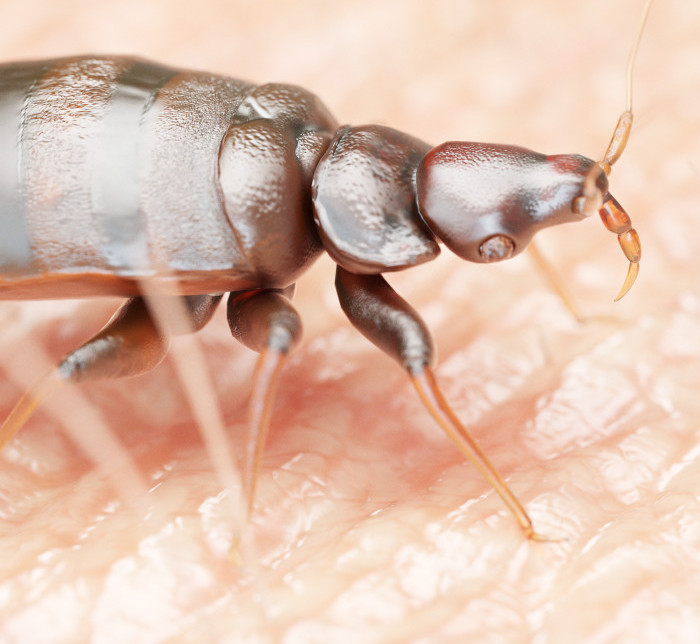
Bed bugs, known for their stealthy feeding habits, primarily operate under the cover of darkness. Their behavior is intricate, revolving around their quest for a blood meal which they need to progress through their life stages.
Feeding Habits
Bed bugs exhibit a distinct preference for darkness during their feeding times, which typically occur at night. Their feeding process involves a piercing mouthpart, which they use to extract a blood meal from their hosts, which can be either animals or humans. The feeding can last from 3 to 10 minutes, and they tend to feed every 5 to 10 days. After feeding, they retreat to their hiding places to digest the meal undisturbed.
- Frequency: Every 5-10 days
- Duration: 3-10 minutes per feeding
- Activity Peak: Nighttime
Habitat Preferences
These insects are highly adaptive and prefer residing in close proximity to their hosts. One may find bed bugs harboring in nearby locations such as loose wallpaper, within objects like furniture, or cracks in the flooring. Their flat body shape allows them to hide in extremely small crevices, making them challenging to detect and eradicate.
- Common Habitats:
- Loose wallpaper
- Cracks in furniture
- Objects close to the sleep area
By gaining an understanding of bed bug behavior, one becomes better equipped in both preventing and controlling potential infestations.
Final Thoughts
Bed bugs are indeed insects, classified within the Cimicidae family. These tiny pests feed on human blood, usually at night, leading to itchy bites and a number of potential psychological impacts. Studies, such as the one highlighted in Psychological effects of bed bug attacks, reveal that infestation can lead to anxiety, stress, and even severe emotional distress in some individuals.
Key characteristics of bed bugs include:
- Size: Small (approximately 5-7mm long)
- Shape: Oval
- Body: Flat and wingless
Bed bugs are adept hitchhikers, making their way into homes via luggage, clothing, and furniture. Once established, they can be difficult to eradicate due to their resistance to common pesticides, as mentioned in the Psychiatric consequences of actual versus feared and perceived bed bug infestations.
It is advised to be vigilant when travelling or acquiring second-hand furniture to prevent bringing these unwelcome guests home. They’re not dangerous in terms of transmitting diseases, but their presence can be quite disturbing and uncomfortable. If one encounters a bed bug infestation, it’s important to seek professional pest control services to effectively deal with the problem.